An act was passed on December 18 in the year 2006 in order to safeguard the forest rights of traditional forest dwellers in India. This act is called as the Scheduled Tribe and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.It is variously addressed as Forest Rights Act, the Tribal Bill, and the Tribal Land Act.
The above Act is related to the rights of communities that live in forests. This Act safeguards their rights on forest land and other forest resources that were earlier denied to them over decades. This condition had remained due to the continuance of the Colonial Forest Laws in the country.
Those who support the Act tell that the act has provisions of making the process of conservation more effective and transparent. The demand of the law for claiming rights on Jal, Jangal, and Zameen was continued since long in the form of various demonstrations on the levels of states and the country. However some persons are in opposition and say that the law will initiate massive forest destruction.
Forests are necessary for the livelihood of humanity and the existence of biodiversity on this earth. It is a well known fact. Still, forests are facing continuous threats resulting into a considerable loss of biodiversity as well.
As per reports at least 17 percent of the rain forests of Amazon have been lost in the last fifty years. It can be easily understood that it may take a very long time to regenerate a forest if it is destroyed. Under the challenging climatic conditions and in the poor soil quality it is very difficult to regenerate a forest by human beings.
One of the most dangerous effects of depletion of forests is the loss of wild animals. According to a report about seventy percent of the land animals on the earth live in forests. They cannot survive if their home is destroyed. The canopies of forest trees, as also of other trees, play important roles in regulating atmospheric temperature. A drastic variation in temperature is sure to occur from day to night if plants and trees are removed.
Unsustainable practices of forestry are basic cause behind the depletion of forests. Deforestation is usually caused through logging, urban development and land conversion for housing and agriculture.

All these practices have been reported to cause an annual loss of more than 130,000 sq. km of forest habitat on global scale. During deforestation a number of animals are at risk of persecution and poaching when they come into conflict with humans.
Many of our forests are regularly exposed to fires. In India forests of Himachal Pradesh and Chhattisgarh are under fire since lost many months. So happens with forests across the globe year after year.
The frequency of forest fires has increased due to human activities. In this way our forests are destroyed directly. In addition forest fires seriously contribute to the atmospheric load of carbon dioxide creating threats to the whole world.
Forests provide numerous benefits to human beings. Though use of all the forest products cannot be stopped altogether, it is important to ensure that forest management is carried out responsibly and sustainably.
One way of doing responsible and sustainable forest management is through Forest Certification. If wood and other forest products are processed, transformed, manufactured, and distributed in sustainable ways, these can be officially labeled. Thus consumers can choose to purchase products that are derived from managed forests.
To overcome the serious loss of deforestation, reforestation and compensatory forestation can be strong measures for human beings to take up. It can counteract to the loss of habitat also. Forests regenerate naturally in some areas. It is either through seeds or through vegetative propagation. Native tree species need to be planted manually in certain areas.
A number of organisations across the world are working hard to regenerate forests and to create Wildlife Corridors especially for elephants. The Wildlife Corridors are stretches of forests created to link patches of forests that are isolated.
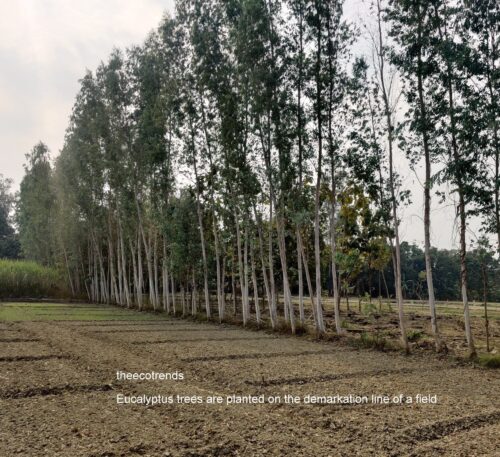
A new trend of planting Eucalyptus trees in rural areas is becoming more popular now a day. Farmers plant Eucalyptus trees on the demarcation lines of their fields. These trees when grown up are sold to paper mills on a fair price.

The Eucalyptus plants are regenerated as a second crop from the cut roots and a good business continues.
Many farmers in rural areas are planting timber trees in their less productive land and sell the trees to timber traders.
Some organisations too have come forward in this direction who takes fields of farmers and plant trees in those fields. They take care of trees for some years. Later they leave the care and management of trees on farmers.